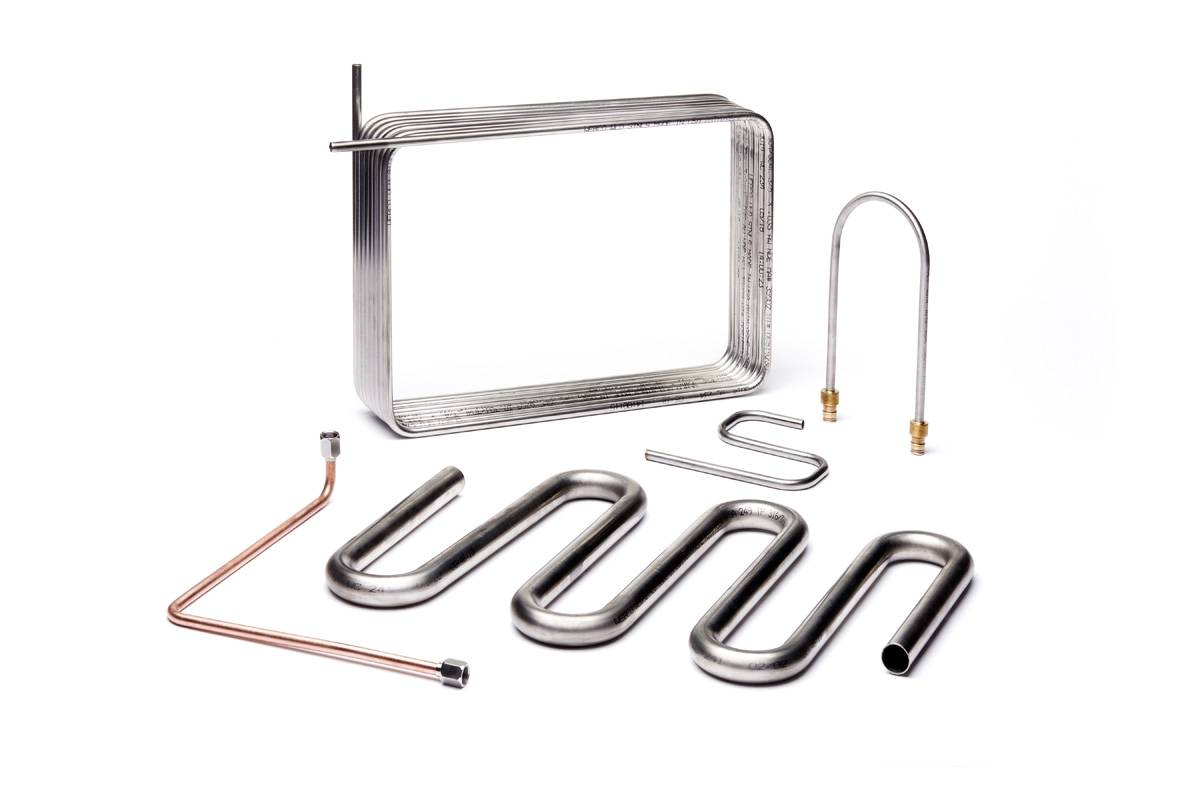
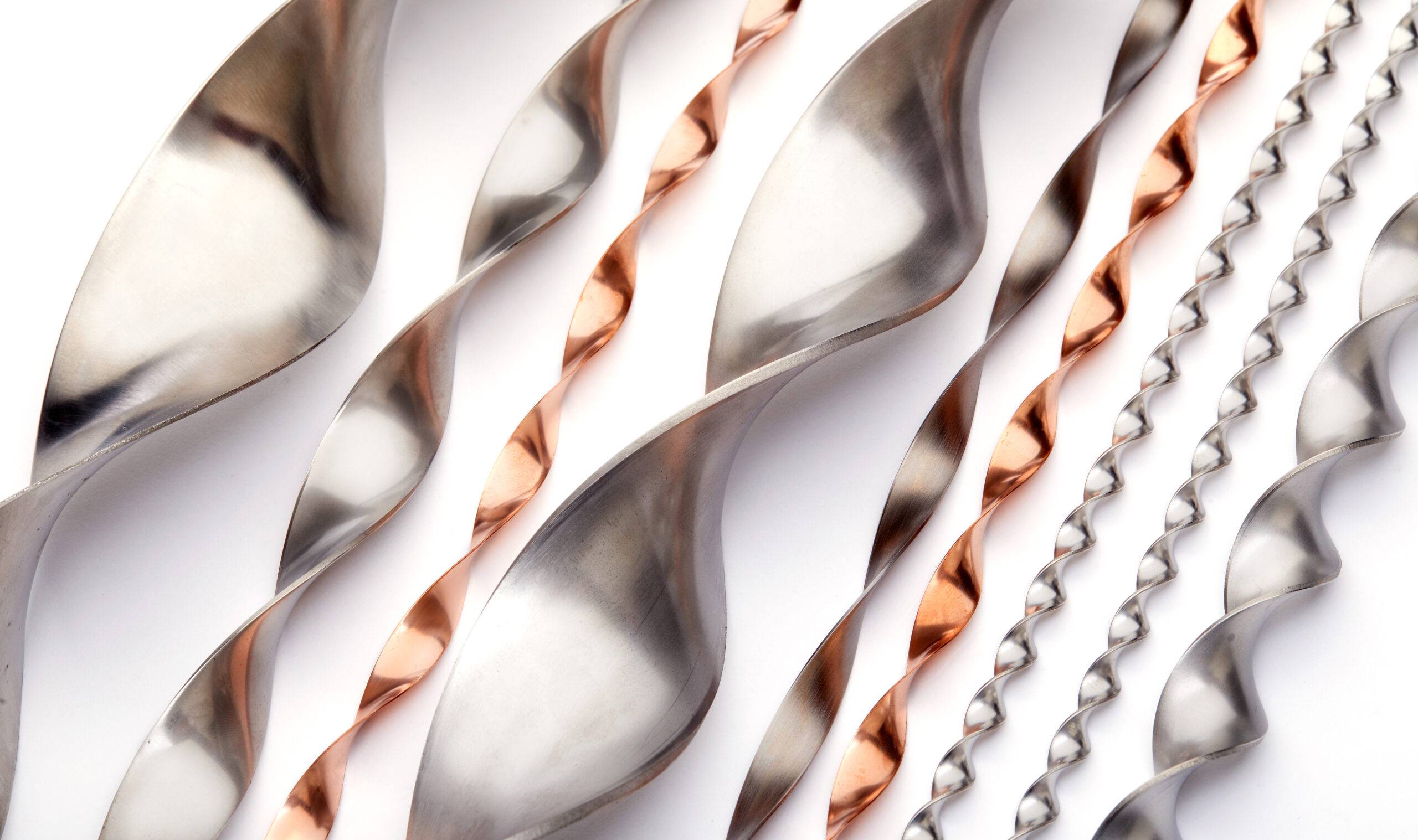
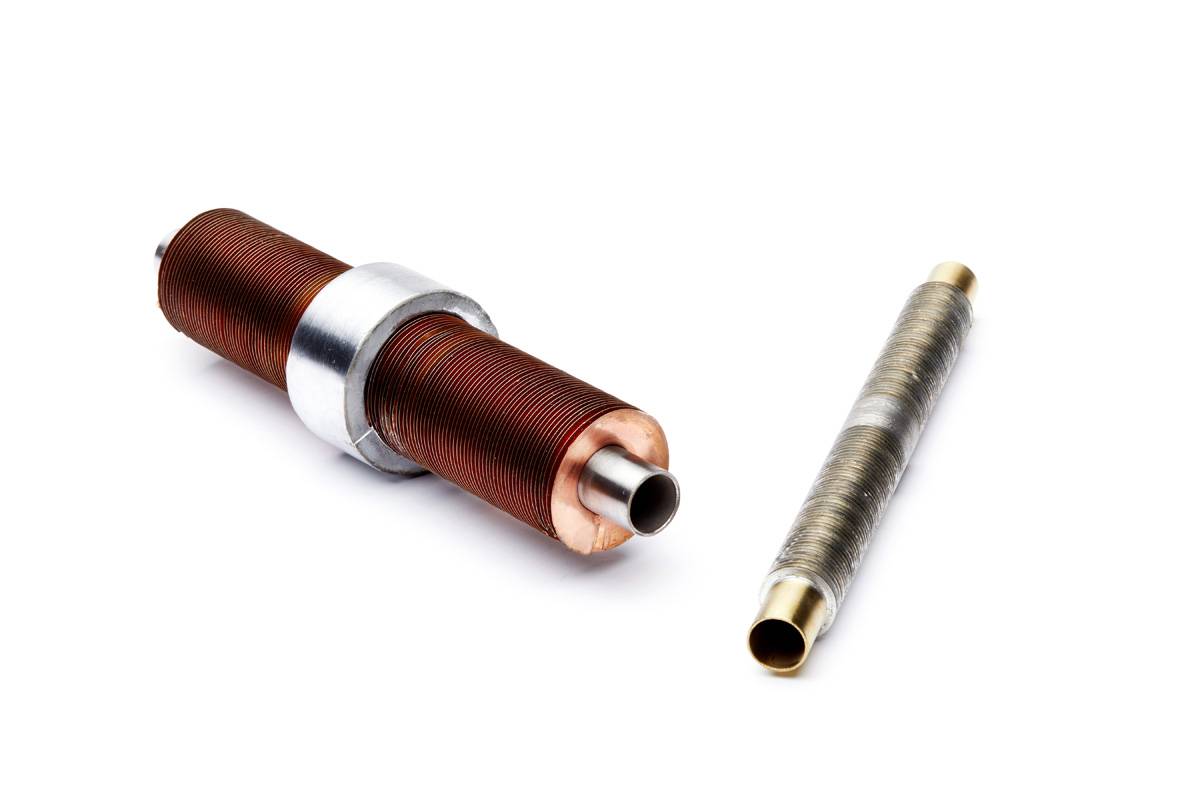
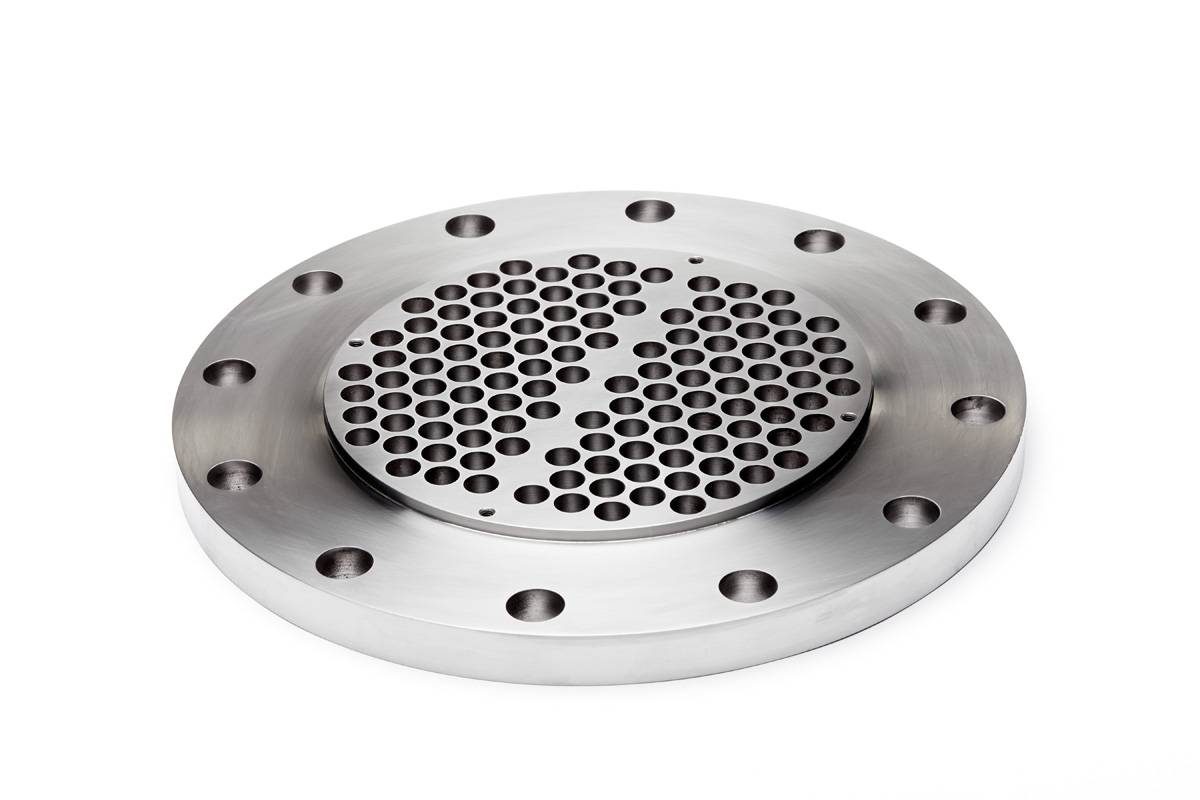
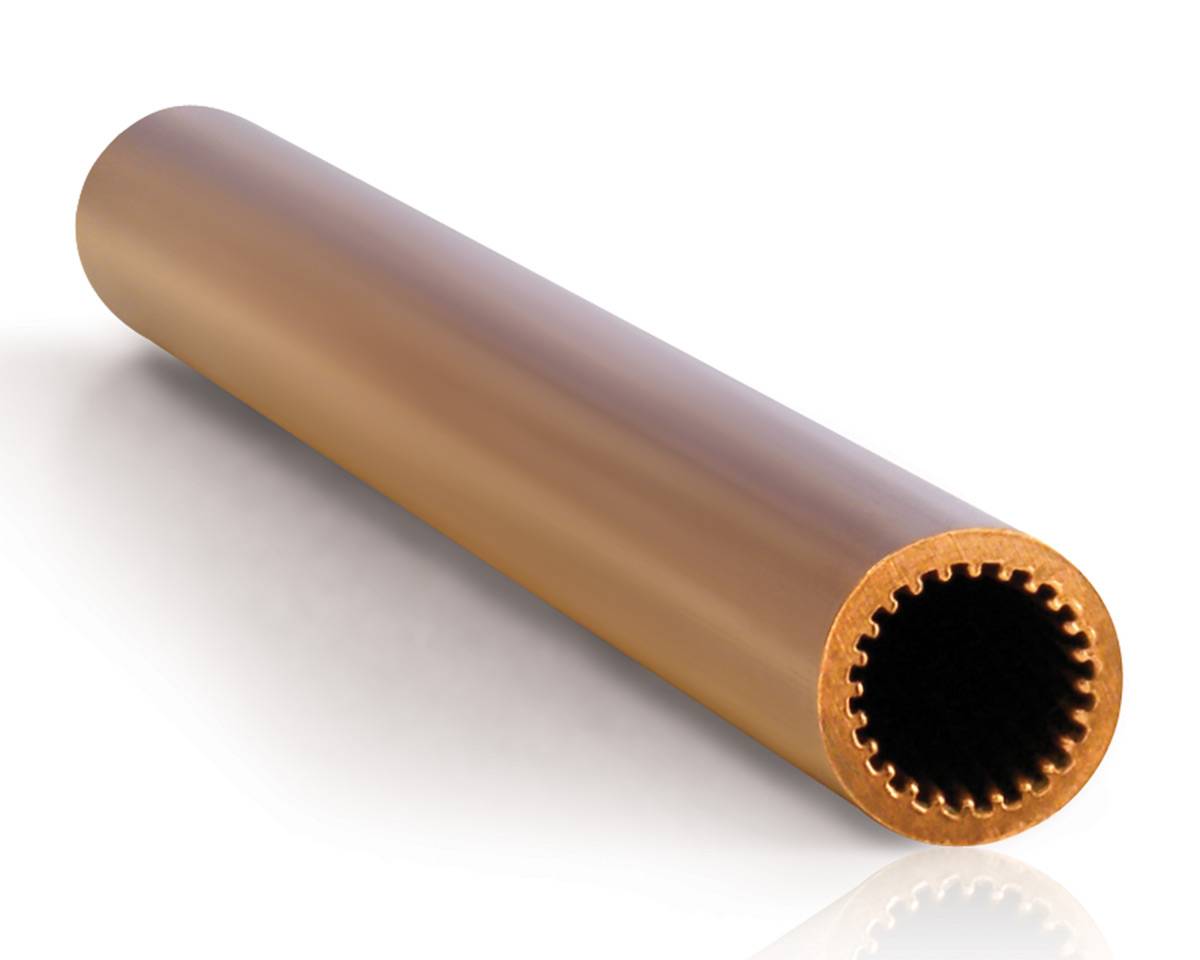
It’s no secret that finned tubes are core components of heat exchangers. After the product’s initial conception nearly a century ago, they continue to be in high demand among buyers. Surely there must be a reason, right?

The Beginnings of Efficiency
In 1933, Edward G. Lehman had a vision: create an efficient way to increase the contact area with external fluid and improve heat transfer coefficients. The Pennsylvania-based inventor received his first patent in September 1934, only to perfect his craft in April 1937. Today, we can find finned tubes in industrial settings, office buildings, and even our own homes.
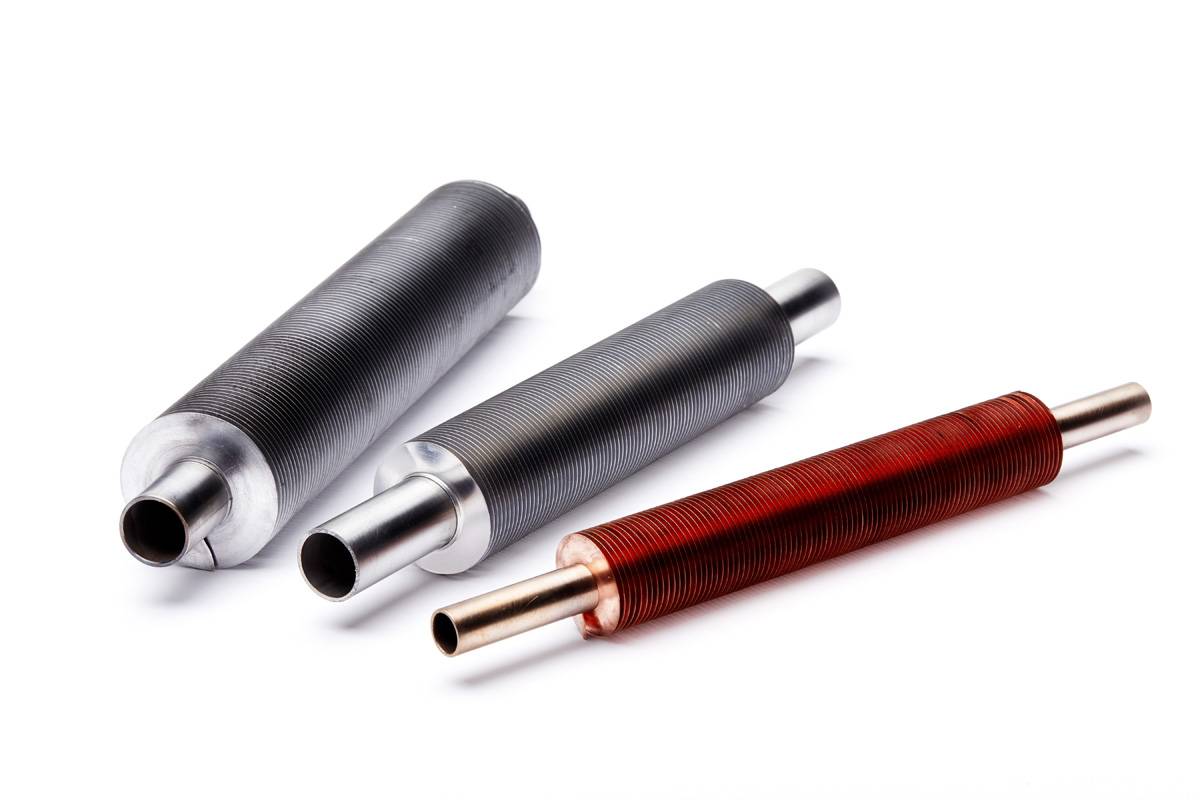
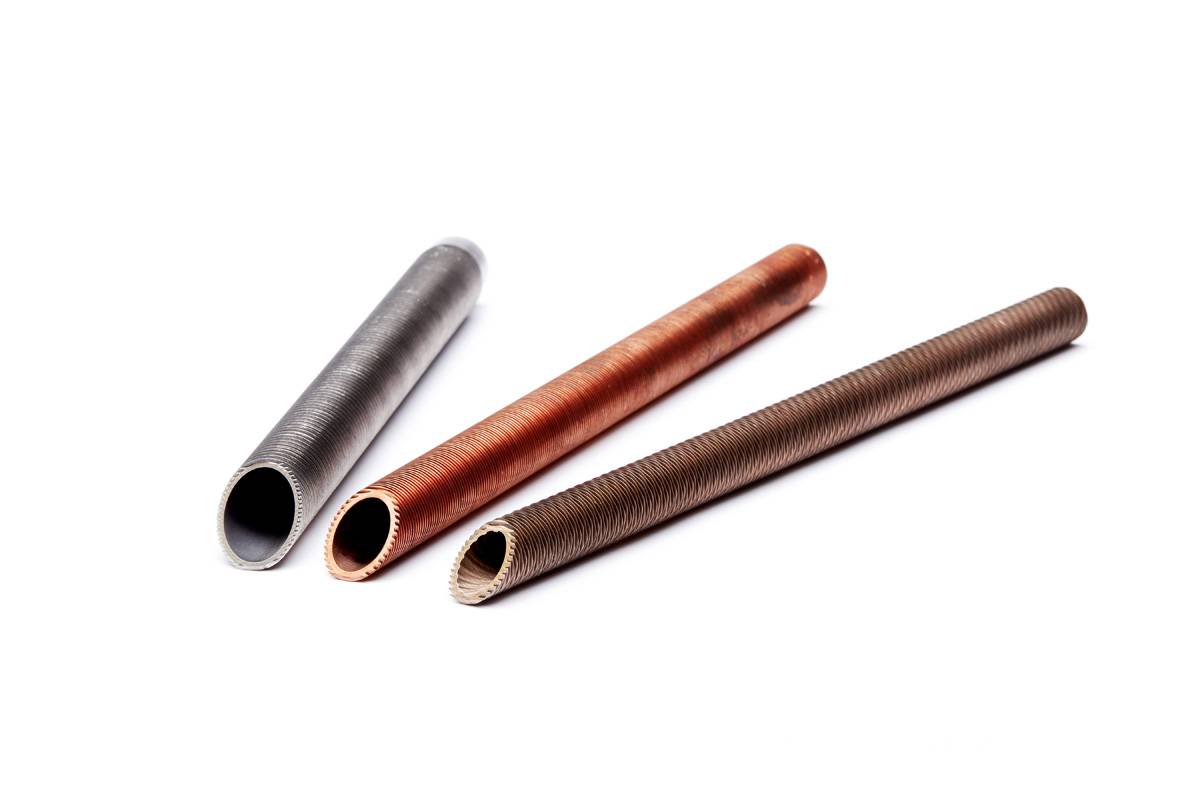
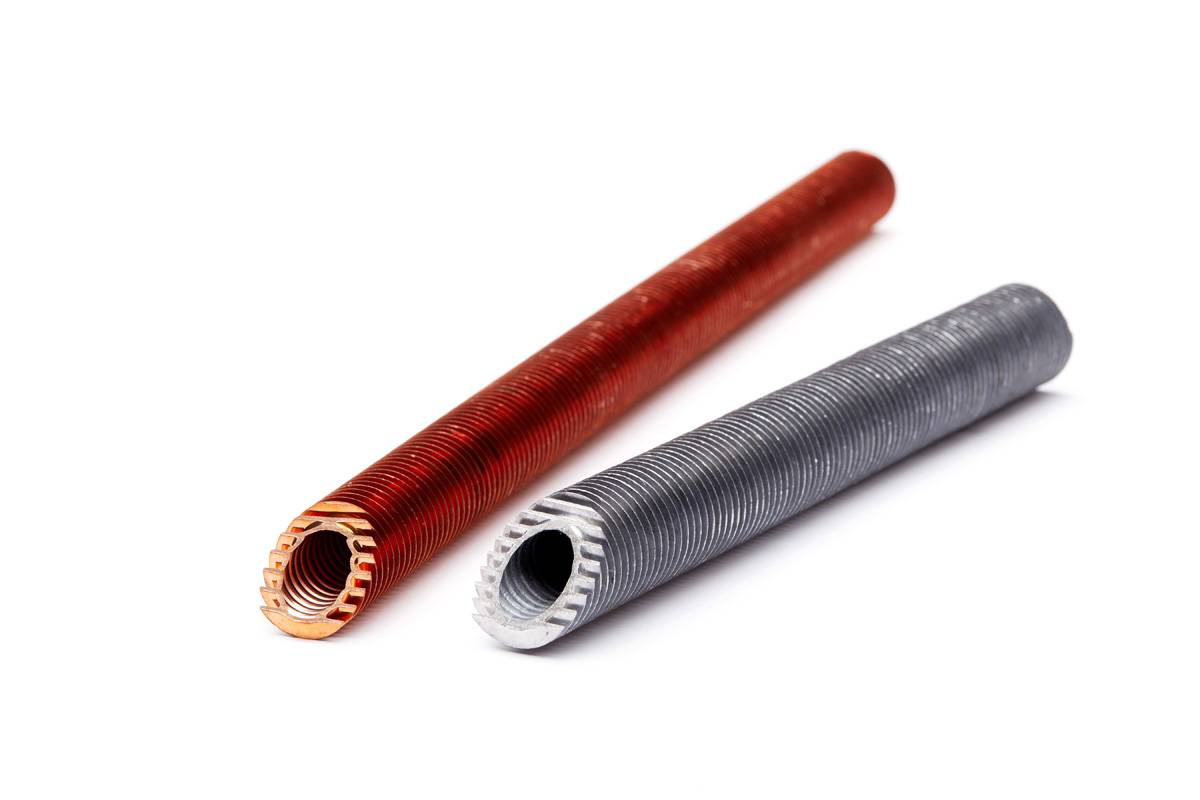
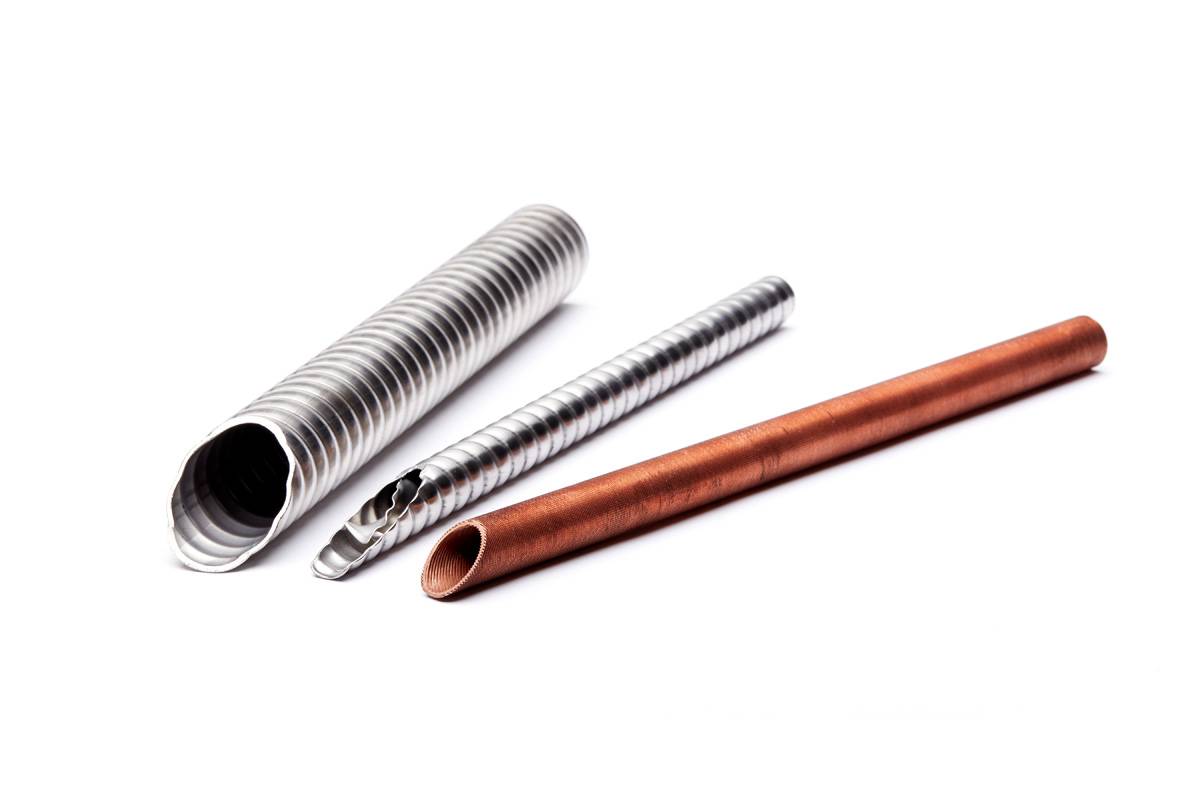
Finned tubes are typically manufactured using one of four metallic elements, each with their own unique advantages and a variety of applications.
Stainless steel: Ideal for corrosive conditions and/or a high temperature.
Carbon steel: Ideal for high temperature applications where corrosion is not an issue.
Aluminum: Ideal for a high heat transfer rate in Air Cooling applications.
Copper: Ideal for the most efficient high heat transfer rate with common metals.
Many finned tubes are also manufactured using alloys.

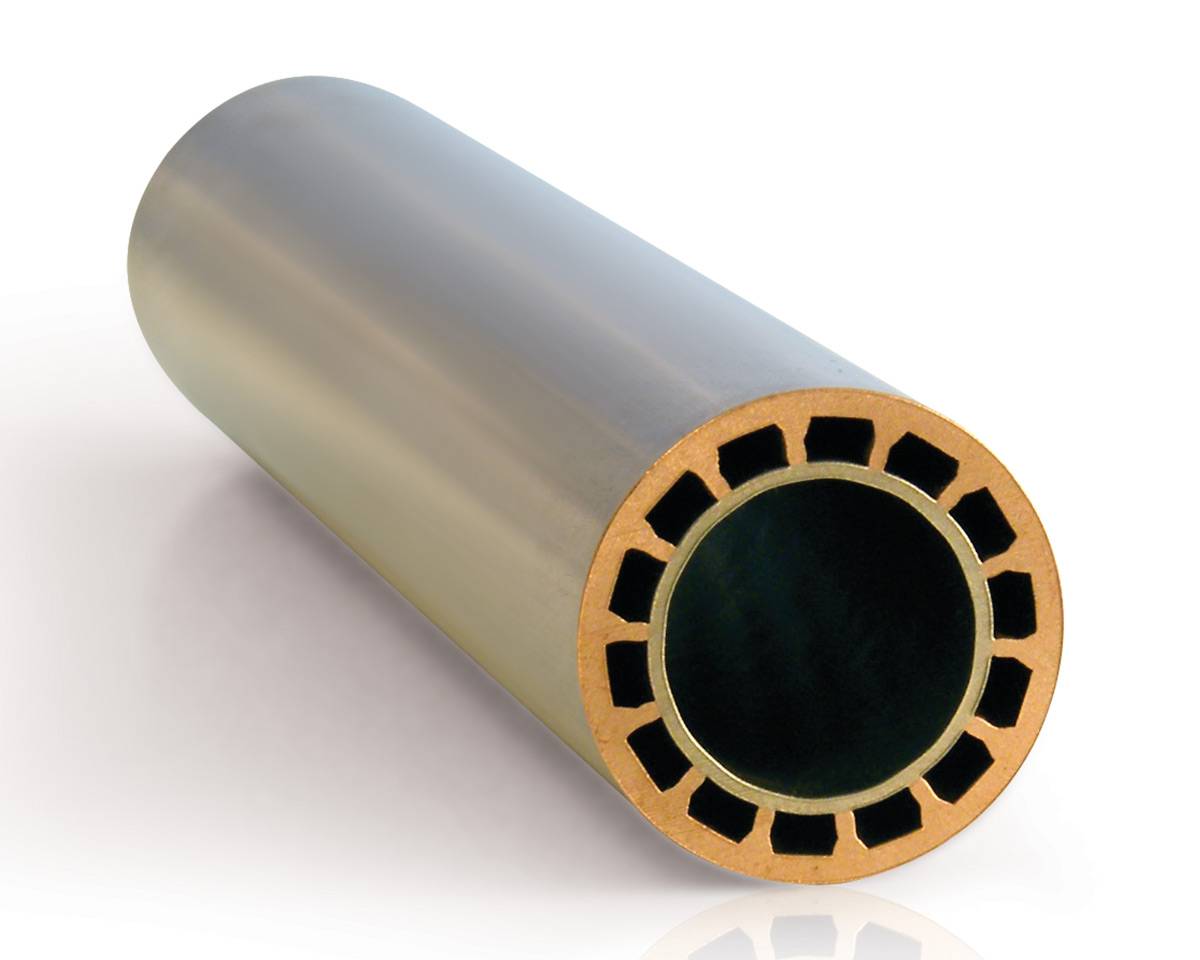
Medium-High finned tube made from mono extruded copper alloys
A Finned Tube Here, A Finned Tube There
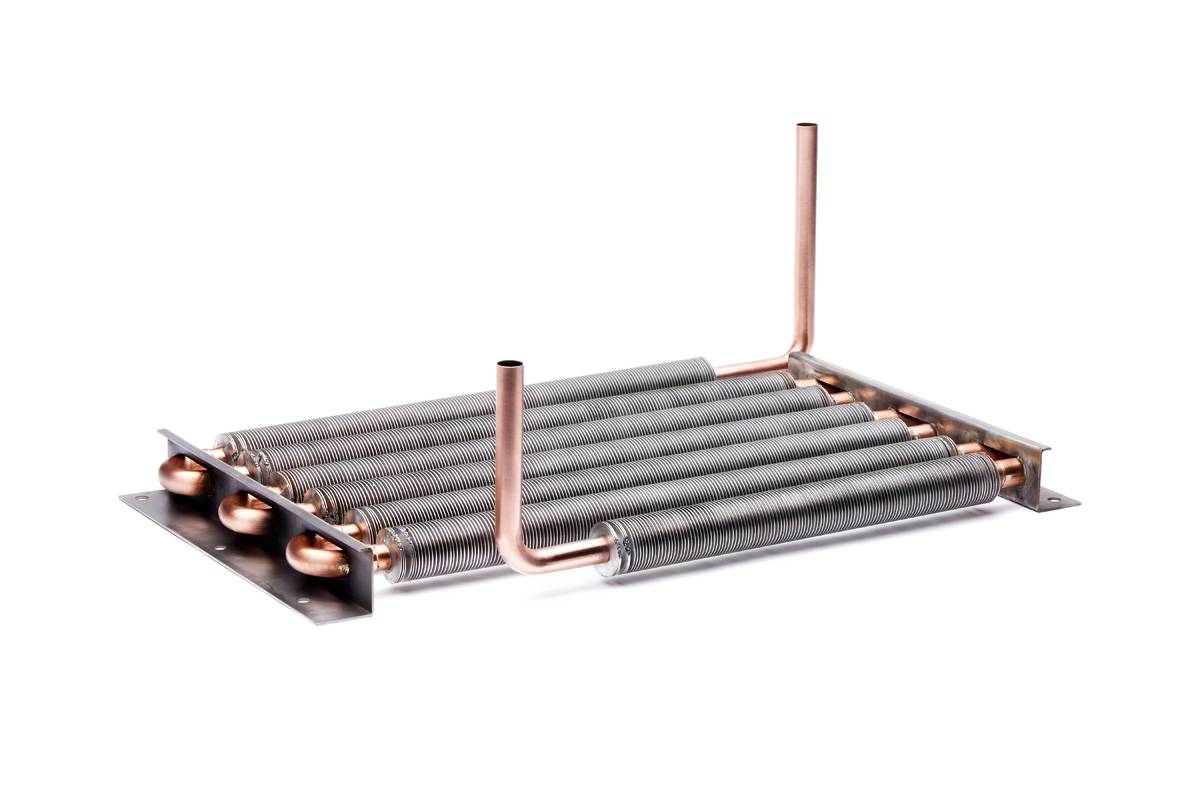
From heated pools and hot tubs to industrial boilers, finned tubes are working their science. Some finned tubes offer multiple functions for increased productivity. In addition to providing hot water for residential and commercial consumers, industrial boilers serve the space heating needs of chilly tenants in apartment buildings, office buildings, and warehouses. Heated pools and hot tubs use hot water from a boiler to keep the chlorinated water at a cozy temperature. There you have it. Finned tubes are used in many ways that improve your life.

The Dura-IB Brazed Edge Tension Finned Tube is perfect for heating pools and hot tubs
Finned Tubes Are Cool
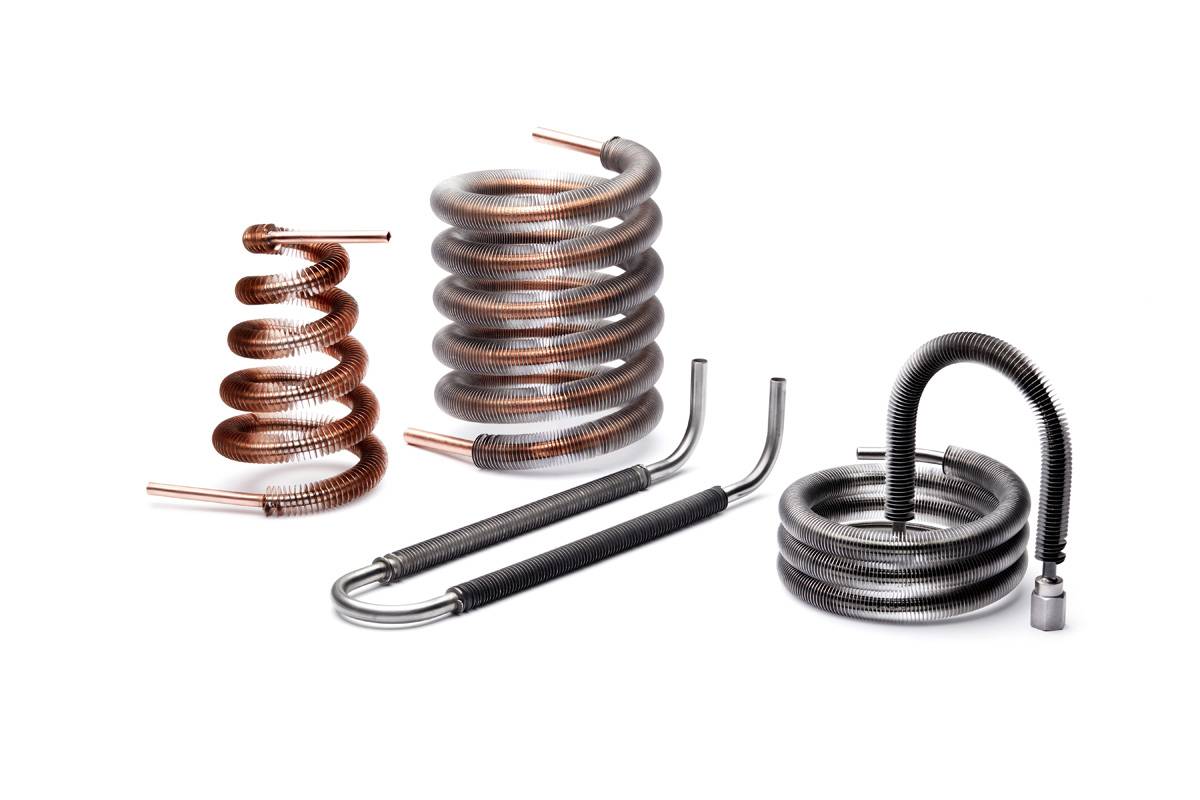
It’s no secret that the capabilities of a finned tube heat exchanger are enough to pique the interest of buyers. Dry cooling is increasing in popularity, primarily due to excess water usage in steam power plants. Many plants are implementing the use of air-cooled heat exchangers to cool the process steam.

The Dura-L Footed Finned Tube is the top choice for dry cooling
Condensers are the hub of outdoor air conditioning units and refrigerators. Through the process of heat transfer, a high-pressure gas (refrigerant) converts to a liquid for effective cooling. Yeah, finned tubes are pretty cool.

Dura-KR Rifled Low Finned Tube promotes better heat transfer in condensers
Finned Tubes Save Money And Resources
The only alternative to a finned tube is a bare metal tube – an inefficient, resource-depleting method that wreaks havoc among the wallets of consumers and plant operations. Along with the promotion of excess water usage in steam power plants, finless tubes can’t take the heat – literally. In comparison with finned tubes, the lack of surface area creates a relatively low range of temperatures.

Finned tubes help conserve water, a valuable resource necessary for the survival of life on Earth
A 2012 comparative analysis determined a finned tube’s shell is lesser than that of a finless tube, ultimately saving sheet material and decreasing spending. If the higher cost of material isn’t enough to deter buyers, finless tubes tend to have issues withstanding intense working conditions for prolonged periods of time. Bottom line: finned tube heat exchangers are more eco-friendly and durable.
Edward G. Lehman’s design continues to prove its efficiency. At Energy Transfer, we believe in upholding his legacy by manufacturing only the most robust of finned tubes for optimal performance. Click here to request a quote, or give us a call at 330-868-3060. One of our representatives will be happy to assist.
Want to not screw up your finned tube project? Our FREE GUIDE tells you everything you need to know. Download yours today